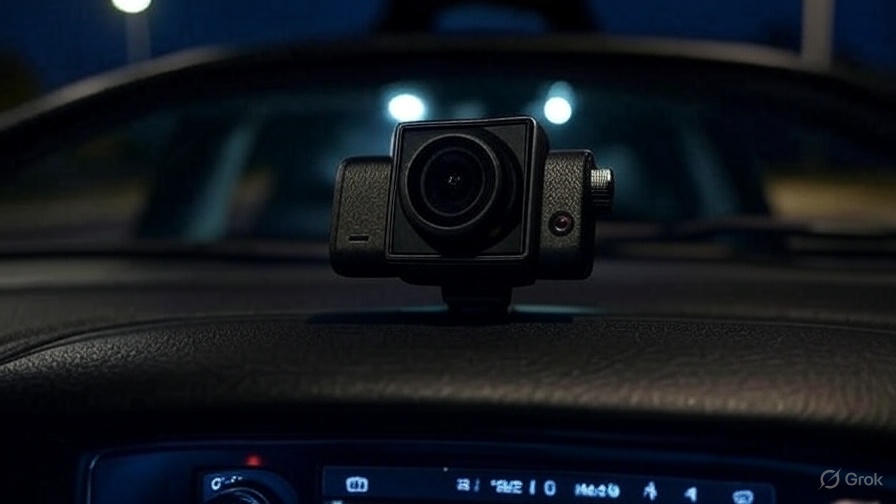
Dashboard cameras have revolutionized the way we document our driving experiences and protect ourselves on the road. These compact devices sit quietly on your windshield, recording everything that happens during your journey. But have you ever wondered about the technology behind these remarkable gadgets?
The mechanics of dash cam operation involve several sophisticated components working together to capture, process, and store video footage. From the moment you start your car to when you park, these devices continuously monitor your surroundings, creating a digital record of your travels.
Contents
- The Basic Components That Make Dash Cams Function
- Power Systems and Installation Methods
- Video Recording Technology and Quality Standards
- GPS Integration and Location Tracking
- Storage Management and Loop Recording
- Advanced Features and Smart Technology
- Connectivity and Mobile Integration
- Image Processing and Enhancement Technologies
- Legal Considerations and Privacy Features
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Future Trends in Dash Cam Technology
- Conclusion
The Basic Components That Make Dash Cams Function
Every dash cam contains essential hardware components that enable it to record high-quality video footage. The image sensor serves as the heart of the device, capturing light and converting it into digital information. Most modern dash cams use either CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) or CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors.
The lens system focuses light onto the image sensor, determining the field of view and image quality. Wide-angle lenses capture more of the road ahead, typically covering 120 to 170 degrees of view. This broad coverage ensures that the camera records not just the vehicle directly in front, but also cars in adjacent lanes and roadside activity.
The processor handles the complex task of converting raw sensor data into compressed video files. Advanced processors enable features like motion detection, parking mode recording, and GPS tracking. These chips also manage the compression algorithms that keep file sizes manageable while maintaining video quality.
Storage components, typically microSD cards, hold the recorded footage. The capacity determines how much video the dash cam can store before overwriting older files. Most devices use loop recording, automatically deleting the oldest footage when storage fills up, ensuring continuous operation without manual intervention.
Power Systems and Installation Methods
Dash cams require a reliable power source to function properly. Most models connect directly to your vehicle’s 12V power outlet or cigarette lighter socket. This connection provides power when the engine runs and automatically shuts off the camera when you turn off the ignition.
Hardwired installations offer more permanent solutions and additional features. Professional installers connect the dash cam directly to your vehicle’s fuse box, enabling parking mode recording and eliminating visible wires. This method allows the camera to monitor your parked vehicle using residual battery power.
Some dash cams include built-in batteries or capacitors for backup power. These components ensure the device continues recording for a few minutes after losing main power, capturing crucial moments like parking incidents or hit-and-run accidents.
The installation process typically involves mounting the camera on your windshield using suction cups or adhesive mounts. The positioning affects recording quality and legal compliance, as many jurisdictions have specific rules about windshield obstructions.
Video Recording Technology and Quality Standards
Modern dash cams record in various resolutions, from standard 1080p Full HD to ultra-high-definition 4K. Higher resolution cameras capture more detail, making it easier to read license plates and identify facial features. However, higher resolution also means larger file sizes and increased storage requirements.
Frame rates determine how smooth the recorded video appears. Most dash cams record at 30 frames per second, providing fluid motion capture. Some models offer 60fps recording for even smoother footage, though this doubles the file size.
Video compression algorithms reduce file sizes while maintaining acceptable quality. H.264 and H.265 codecs are common choices, with H.265 offering better compression efficiency. The compression level affects both storage requirements and video quality, requiring manufacturers to balance these competing needs.
Night vision capabilities rely on specialized sensors and processing algorithms. Some dash cams use infrared technology, while others employ larger sensors that capture more light. Advanced models feature Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) technology, which balances exposure across different lighting conditions in the same frame.
GPS Integration and Location Tracking
GPS functionality adds valuable context to dash cam recordings. The GPS receiver determines your exact location, speed, and direction of travel. This information gets embedded in the video files, creating a comprehensive record of your journey.
The GPS data proves invaluable during insurance claims and legal proceedings. It provides objective evidence of your speed and location when incidents occur. Some dash cams display this information as an overlay on the video, showing real-time speed and coordinates.
GPS also enables advanced features like automatic time and date synchronization. The system ensures accurate timestamps on all recordings, eliminating confusion about when events occurred. This synchronization happens automatically whenever the device connects to GPS satellites.
Route tracking allows you to review your complete journey on a map. Dedicated software applications display your route alongside the corresponding video footage, making it easy to locate specific incidents or landmarks.
Storage Management and Loop Recording
Loop recording represents one of the most important features of dash cam technology. This system automatically overwrites the oldest video files when storage space runs low, ensuring continuous operation without user intervention.
The loop recording system divides storage into segments, typically 1, 3, or 5-minute video clips. When storage reaches capacity, the system deletes the oldest segment and creates a new one. This process continues indefinitely, maintaining a rolling archive of recent footage.
File protection mechanisms prevent important footage from being overwritten. Most dash cams include G-sensors that detect sudden impacts or rapid deceleration. When triggered, these sensors lock the current video file, protecting it from the loop recording process.
Manual file protection allows users to save specific clips. A button press during recording or playback locks the current file, ensuring preservation of important evidence. Some models offer voice control for hands-free file protection.
Advanced Features and Smart Technology
Motion detection technology enables parking mode recording without draining your vehicle’s battery. The camera monitors the scene for movement and begins recording when activity is detected. This feature helps capture parking lot incidents and vandalism attempts.
Time-lapse recording compresses long periods into short video clips. This feature proves useful for documenting extended parking periods or long road trips. The camera captures frames at regular intervals, creating a condensed version of events.
Collision detection systems use accelerometers and gyroscopes to identify sudden impacts. These sensors trigger automatic file protection and can send alerts to connected smartphones. Some advanced models differentiate between minor bumps and significant collisions.
Lane departure warnings and forward collision alerts add active safety features to dash cams. These systems analyze the video feed in real-time, alerting drivers to potential hazards. While not as sophisticated as dedicated safety systems, they provide additional awareness.
Connectivity and Mobile Integration
Wi-Fi connectivity allows dash cams to communicate with smartphones and tablets. This wireless connection enables video playback, settings adjustment, and file transfer without removing the memory card. Many manufacturers offer dedicated mobile apps for remote camera control.
Bluetooth connectivity provides another wireless option for some models. This connection typically supports audio recording and hands-free operation. Some dash cams can connect to your phone’s GPS for enhanced location accuracy.
Cloud storage services offer automatic backup of important footage. These services upload protected files to remote servers, ensuring evidence preservation even if the dash cam is damaged or stolen. Subscription services typically offer limited free storage with paid upgrades available.
Live streaming capabilities allow remote monitoring of your vehicle. Some dash cams can stream video to your smartphone or computer, enabling real-time viewing from anywhere with internet access. This feature proves valuable for fleet management and vehicle security.
Image Processing and Enhancement Technologies
Digital image stabilization reduces camera shake and vibration effects. This technology analyzes the video feed and applies corrections to smooth out unwanted movement. The result is clearer, more stable footage that’s easier to analyze.
Automatic exposure control adjusts camera settings based on lighting conditions. This system ensures optimal image quality in various environments, from bright sunlight to dark tunnels. Advanced models use multiple exposure zones for better overall balance.
Noise reduction algorithms minimize graininess in low-light conditions. These systems analyze the video feed and apply filtering to reduce digital noise while preserving important details. The result is cleaner footage in challenging lighting situations.
Color correction technology ensures accurate color reproduction across different lighting conditions. This feature proves important for evidence purposes, as accurate colors help with vehicle identification and other forensic analysis.
Legal Considerations and Privacy Features
Privacy protection features address growing concerns about surveillance technology. Many dash cams include privacy zones that can be blocked from recording. These features allow users to protect sensitive areas while maintaining security coverage.
Audio recording capabilities raise additional privacy considerations. Most dash cams can record audio from inside the vehicle, but this feature may be restricted in certain jurisdictions. Users should understand local laws regarding audio recording consent.
Timestamp accuracy becomes crucial for legal evidence. Many dash cams sync with GPS satellites for precise time information. This synchronization ensures that recorded events have legally admissible timestamps.
Data encryption protects recorded footage from unauthorized access. Some high-end models encrypt video files, ensuring that only authorized users can view the content. This feature proves valuable for commercial fleets and security-conscious individuals.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance keeps dash cams operating at peak performance. Memory card formatting prevents corruption issues and maintains optimal write speeds. Most manufacturers recommend monthly formatting to prevent data problems.
Lens cleaning affects video quality significantly. Road dust, fingerprints, and weather residue can degrade image clarity. Regular cleaning with appropriate materials ensures clear footage capture.
Firmware updates add new features and fix known issues. Many dash cams support over-the-air updates through Wi-Fi connections. These updates can improve performance, add features, and address security vulnerabilities.
Temperature management prevents overheating damage. Dash cams operate in challenging environments, from freezing winters to scorching summers. Proper ventilation and thermal management ensure reliable operation across temperature extremes.
Future Trends in Dash Cam Technology
Artificial intelligence integration promises smarter dash cam functionality. AI algorithms can identify specific events, objects, and behaviors automatically. This technology could revolutionize incident detection and evidence analysis.
5G connectivity will enable faster data transfer and real-time video streaming. This technology could support immediate emergency response and remote monitoring capabilities. Higher bandwidth will also enable cloud-based processing and storage.
Enhanced sensor fusion combines multiple data sources for better situational awareness. Future dash cams might integrate radar, lidar, and other sensors for comprehensive environmental monitoring. This technology could provide advanced driver assistance features.
Improved battery technology will extend parking mode operation and reduce dependence on vehicle power. Longer-lasting batteries could enable continuous monitoring without draining vehicle batteries or requiring hardwired installations.
Conclusion
Dashboard cameras represent sophisticated technology packages that combine optics, electronics, and software to create reliable driving companions. These devices capture, process, and store video evidence while providing additional safety and security features.
The technology behind dash cams continues evolving rapidly, with manufacturers adding new features and improving existing capabilities. From basic video recording to advanced AI-powered analysis, these devices offer increasingly comprehensive solutions for modern drivers.
Understanding how dash cams work helps users make informed purchasing decisions and maximize the benefits of their investment. Whether you need basic incident documentation or advanced fleet management capabilities, there’s a dash cam solution designed to meet your specific requirements.
The future of dash cam technology promises even more advanced features and capabilities. As these devices become more intelligent and connected, they’ll play increasingly important roles in vehicle safety, security, and documentation. Investing in quality dash cam technology today provides immediate benefits while preparing for tomorrow’s enhanced capabilities.